Magento 2 is one of the most robust ecommerce platforms available today, built to scale and adapt to business needs. At the center of its flexibility is the Magento REST API, which allows developers to connect Magento with external systems, automate tasks, and enhance store capabilities without touching the front end.
For those working with Magento in any capacity—developers, store operators, or integration specialists—understanding how the REST API functions can lead to more efficient workflows and smoother system operations. This guide provides a structured overview of what the REST API offers, how to use it effectively, and why it continues to serve as a vital tool in Magento-based ecosystems.
What Is the Magento REST API?
The Magento REST API is a set of HTTP-based interfaces that allow external applications to interact with the Magento backend. These interfaces support operations like retrieving product information, updating customer records, managing orders, and more.
The API follows REST principles, meaning data is accessed through standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. It supports both JSON and XML formats, though JSON is more commonly used in modern implementations.
Core Use Cases for the REST API
1. Product Management
Adding, updating, or deleting products can be handled via the REST API. This is especially useful for syncing inventory between Magento and external ERPs or PIM systems.
2. Customer Data Integration
Customer accounts, addresses, and activity logs can be pulled or updated remotely. This allows CRMs or marketing platforms to remain in sync with store data.
3. Order and Invoice Automation
Orders, invoices, shipments, and refunds can be retrieved and modified via API. This supports real-time updates to shipping software, accounting platforms, and warehouse systems.
4. Third-Party App Integrations
Connecting Magento to third-party applications—like payment gateways, email platforms, or analytics dashboards—often relies on the REST API to exchange data securely and reliably.
Authentication and Access
The API supports several types of authentication, each suited to different scenarios:
- OAuth 1.0a: Used for applications acting on behalf of users.
- Token-based (Bearer Token): Common for admin-based applications with backend access.
- Session-based (Cookie Authentication): Typically used for frontend experiences involving logged-in users.
Each method requires the right permission configuration to ensure data is protected while keeping the connection functional.
Exploring Common Endpoints
Magento’s REST API organizes endpoints by functional areas. Here are a few examples:
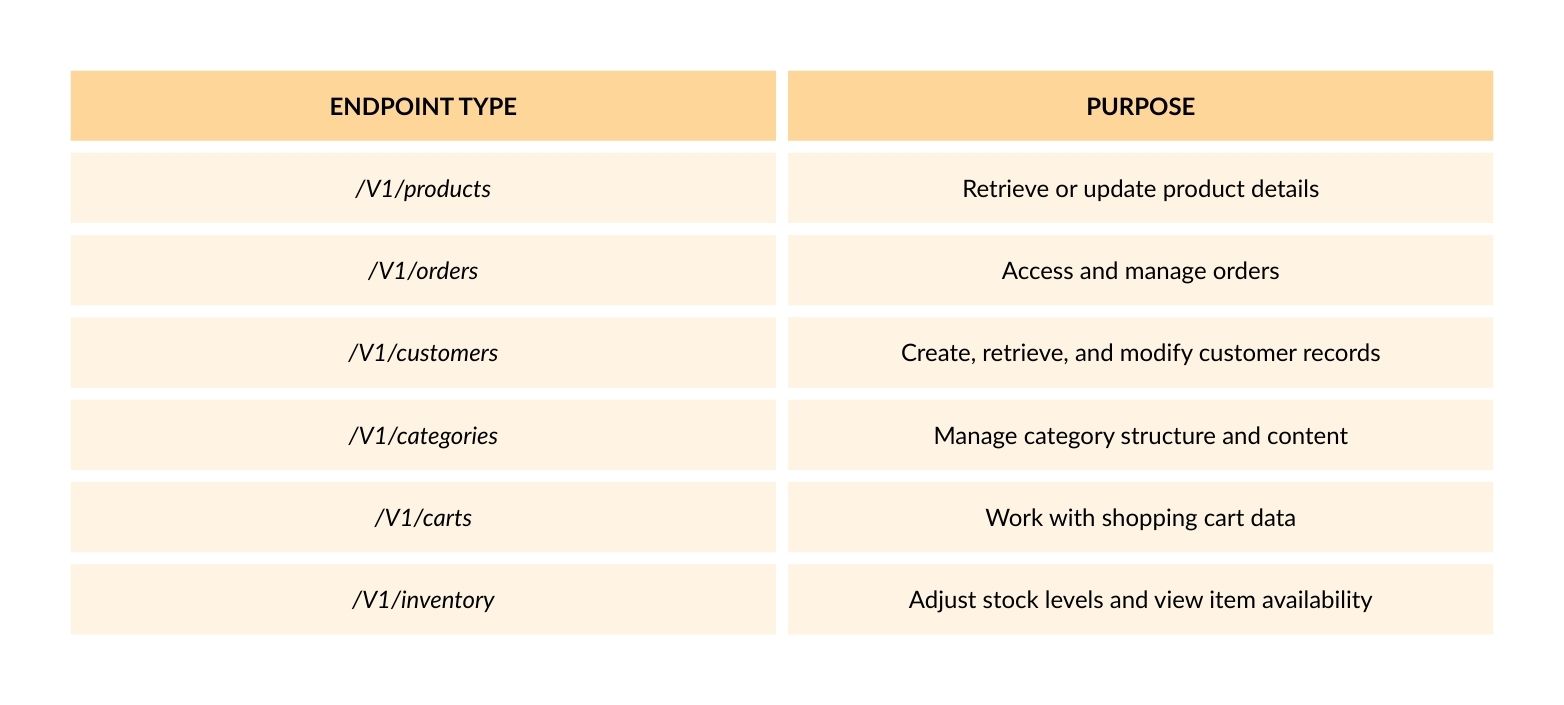
Each endpoint supports specific methods depending on the allowed actions—some permit only GET, while others support full CRUD operations.
Practical Implementation Tips
Start with a Sandbox
Working within a staging or development environment ensures safe experimentation. Errors in API logic can lead to unintended deletions or data corruption if applied directly to live stores.
Use Tools for Testing
Postman and Swagger UI are popular tools for testing REST endpoints. Magento includes its own Swagger-based API documentation accessible via the /swagger route.
Respect Rate Limits
While Magento doesn’t impose strict API throttling by default, high-volume calls can strain server resources. Implement efficient queries and batching where possible.
Enable and Monitor Logs
Magento allows logging of API calls. This can help track usage, debug errors, or audit external system access.
Common Challenges and Fixes
Authentication Errors
Token mismanagement is a frequent issue. Ensure tokens are refreshed correctly and tied to the right user roles.
Caching Delays
Magento’s full-page caching or external CDN layers may not reflect API updates instantly. Clearing caches after updates or using cache-busting methods can prevent stale data issues.
Data Validation Failures
API calls that include incomplete or mismatched data can result in validation errors. Ensure that all required fields are submitted and formats match Magento’s expectations.
Permission Denials
If endpoints return “access denied,” verify that the API user role has correct ACL (Access Control List) settings. Admin roles should be audited regularly for correct scope assignments.
Customizing the Magento API
Magento allows extending the API by creating custom endpoints. This enables business-specific workflows that the core API does not support.
Example use cases:
- Exposing loyalty point balances to a mobile app
- Creating custom order exports for a logistics provider
- Allowing suppliers to update stock for specific SKUs via a restricted endpoint
Custom endpoints require backend development and adherence to Magento’s API schema, but once configured, they follow the same access and format rules as core endpoints.
Security Considerations
Exposing Magento via the API increases the attack surface, so security should be treated seriously.
Best practices include:
- Using HTTPS for all API traffic
- Implementing IP whitelisting for trusted systems
- Keeping all tokens secure and regenerating periodically
- Auditing API roles to avoid unnecessary permissions
- Applying firewall rules to protect admin and customer endpoints
When to Choose REST Over GraphQL
Magento also supports GraphQL for frontend querying. However, REST remains a better fit in certain cases:
- Backend system integrations (ERP, CRM, etc.)
- Batch data updates (bulk product import, mass stock changes)
- Mobile app development that doesn’t require nested querying
- Situations where stable documentation and widespread support are critical
GraphQL is ideal for custom storefronts with complex data relationships, while REST remains more consistent for transactional use cases.
Conclusion
The Magento REST API provides powerful options for customizing, automating, and integrating ecommerce functions. It remains a preferred method for working with backend systems and data-heavy processes. By understanding the structure of endpoints, following authentication best practices, and maintaining careful control over access, the API can support large-scale operations without complexity spiraling out of control.
Used properly, it allows for seamless coordination between Magento and the systems that support customer experience, inventory flow, and fulfillment accuracy. For development teams, marketing analysts, and store managers alike, the Magento REST API remains a tool worth learning and implementing with intent.

