SEO migration means moving your website to a new platform or structure without losing the search visibility you’ve worked hard to build. For Magento stores, this process can be especially challenging. Even one overlooked detail can cause rankings to drop and traffic to nosedive. In this guide, we’ll look at the most common SEO migration mistakes that can damage Magento performance and how to avoid them before you hit launch.
What Is SEO Migration and Why Magento Makes It Tricky
SEO migration aims to maintain your existing visibility in search while you move to a new site or platform. For Magento store owners, that’s a delicate process. Migrations from Magento 1 to Magento 2 bring a mix of URL rewrites, extensions, and intricate category structures that increase the risk of technical errors.
With Magento’s dynamic setup, one overlooked redirect or missing canonical tag can lead to ranking losses. The key is to approach SEO migration as a structured, technically managed project from the start.

Top 10 SEO Migration Mistakes That Destroy Magento Rankings
Mistake #1: Failing to Map and Preserve URL Structure
The issue:
Launching your new site with completely different URLs.
When URLs change without proper mapping, search engines and backlinks pointing to old URLs lead to 404 errors, which destroy ranking equity.
Example:
Old URL: /women/dresses/blue-midi-dress.html
New URL: /products/blue-midi-dress
Without a redirect or mapping file, search engines see the old URL as gone.
How to fix it:
- Crawl your existing site using tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb.
- Create a one-to-one mapping for every product, category, and content page.
- Keep your old redirects active for at least a year.
- Use consistent URL patterns wherever possible.
Mistake #2: Poor 301 Redirects and Redirect Chains
The issue:
Using the wrong redirect type or chaining multiple redirects.
Redirect chains dilute link equity and slow crawling. Sending everything to the homepage also confuses Google and your users.
Example:
/old-category/page.html → /new-cat/page.html → /clean/page.html
How to fix it:
- Always use 301 permanent redirects instead of 302 temporary ones.
- Redirect to the final page directly, not through multiple hops.
- Never redirect unrelated pages to the homepage.
- Test all redirects in bulk before launch.
Mistake #3: Losing Metadata and Structured Markup
The issue:
Titles, meta descriptions, alt text, and schema data often disappear during migration.
This can result in lower click-through rates and loss of structured snippets in Google results.
Example:
A product with a review schema showing star ratings loses its markup after migration, dropping visibility and CTR.
How to fix it:
- Export all metadata before migration.
- Reapply it in the new Magento templates.
- Restore structured data such as product, review, and breadcrumb markup.
- Test with Google’s Rich Results tool after launch.
Mistake #4: Ignoring Internal Links and Anchor Text
The issue:
Old internal links continue pointing to outdated URLs or use inconsistent anchor text.
This breaks the flow of link equity and disrupts navigation for users and crawlers.
How to fix it:
- Use a crawler to identify internal links to old URLs.
- Update all internal links, menus, breadcrumbs, and widgets.
- Keep anchor text relevant and descriptive.
- Ensure Magento’s URL rewrite settings remain clean and consistent.
Mistake #5: Blocking Crawlers or Misusing Robots Rules
The issue:
Accidentally blocking important areas of your site or using noindex tags incorrectly.
If your robots.txt or meta tags prevent crawling, Google cannot index your new pages.
Example:
Leaving a noindex tag on category pages or blocking /media/ paths that serve essential content.
How to fix it:
- Compare old and new robots.txt files line by line.
- Allow all essential directories for crawling.
- Remove unintentional noindex tags.
- Test crawlability in Google Search Console.
Mistake #6: Forgetting to Update Sitemaps and Search Console
The issue:
Old sitemaps often point to outdated URLs.
Without a current sitemap, Google takes longer to discover new content and might keep old URLs indexed.
How to fix it:
- Generate a new XML sitemap after migration.
- Submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Verify your correct property version (HTTPS, www/non-www).
- Use the URL Inspection tool to request indexing of key pages.
Mistake #7: Overlooking Page Speed and Performance
Magento sites are resource-heavy, and a slow site can significantly affect SEO. Poor caching, large images, or unoptimised code slow down load times and reduce crawl efficiency.
How to fix it:
- Configure caching with Redis, Varnish, or full-page cache.
- Use image compression and lazy loading.
- Implement a CDN for static assets.
- Test performance using Lighthouse or GTmetrix.
Mistake #8: Duplicate Content and Missing Canonical Tags
Magento’s layered navigation often creates multiple parameterised URLs for the same product or category. This causes duplicate content issues and splits ranking power.
How to fix it:
- Add canonical tags to variant or filtered pages.
- Manage faceted URLs in Search Console.
- Block irrelevant parameter pages if needed.
- Use “noindex, follow” for pages that should remain accessible but not indexed.
Mistake #9: Skipping Staging, QA, and Monitoring
Launching without testing can lead to unnoticed technical issues that harm rankings immediately.
How to fix it:
- Always run migrations on a staging environment first.
- Conduct full QA on redirects, metadata, structured data, and speed.
- Use annotations in analytics to track performance post-launch.
- Monitor Search Console daily for new errors.
Mistake #10: Excluding SEO from the Migration Team
Leaving SEO specialists out of planning is one of the biggest reasons migrations fail. Developers focus on functionality, while SEOs ensure search visibility remains intact.
How to fix it:
- Involve SEO experts at every stage, from mapping to testing.
- Create a shared migration checklist for developers and marketers.
- Validate SEO requirements before final sign-off.
- Treat Magento SEO as an ongoing part of your migration, not an afterthought.
How to Recover If Rankings Drop
Even with careful planning, rankings can dip temporarily after migration. Follow these recovery steps:
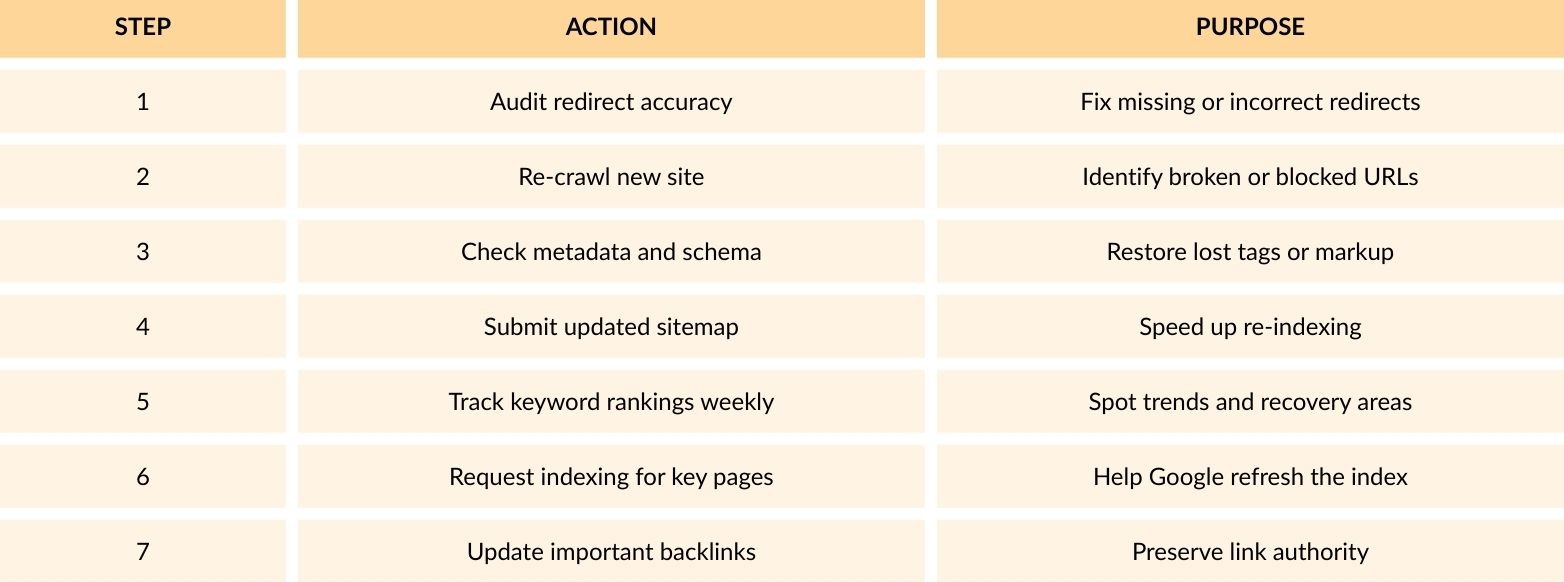
Monitor recovery over 4–8 weeks. If rankings remain unstable, conduct a technical SEO audit to locate hidden crawl or indexation issues.
Conclusion
SEO migration mistakes can destroy Magento rankings, but most of them are completely avoidable. The key is preparation. Map your URLs, test redirects, retain metadata, check crawlability, and include SEO experts throughout the process. If handled correctly, SEO migration can protect your traffic and even improve performance on your new Magento store.
If you are planning a move or a Magento migration, the 5MS can help ensure your transition is smooth, data-driven, and ranking-safe.

